
 |
Here we illustrate how the same four techniques we just studied for shape approximating curves can be applied to shape approximating tensor product surfaces.
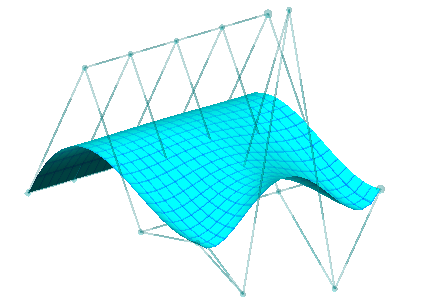
| The 4x3 Bezier surface from the previous page | The new (red) degree 4x3 surface was grafted onto the previous with C1 continuity |
|
|
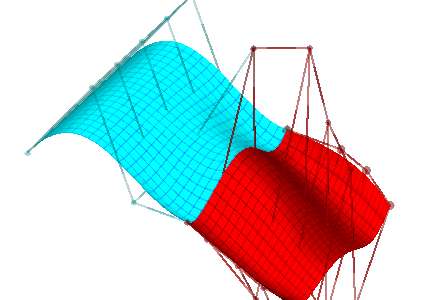
| We start again with our original degree 4x3 surface | Now we subdivide in the s parametric direction; the red and cyan pieces, taken together, exactly reproduce the original surface |

|
|
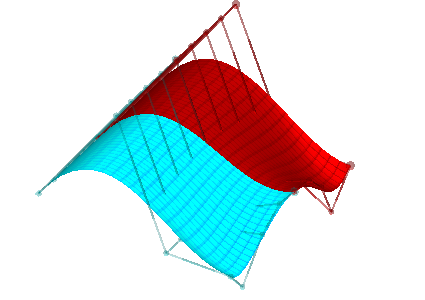
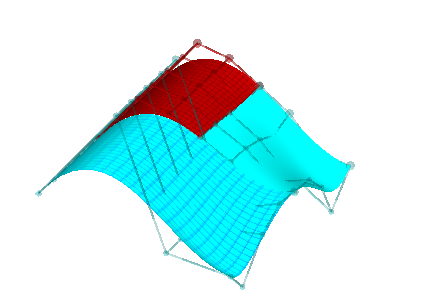
| Now we subdivide the red piece in the t parametric direction; the red piece and the cyan piece without grid lines exactly reproduce the red piece in the previous step | Finally we subdivide the cyan piece with grid lines in the t parametric direction; the resulting four patches (two with grid lines and two without) exactly reproduce the original degree 4x3 surface; as we have seen with curves, any of the pieces can now be independently adjusted; C1 is preserved as long as we don't adjust points along or adjacent to the seams |
 |
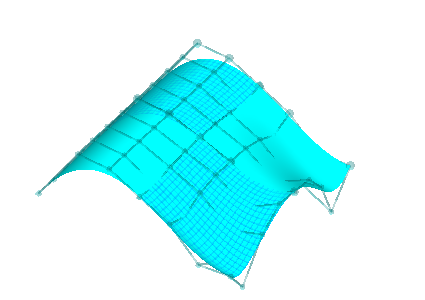
|
| Back to our original degree 4x3 Bezier surface | The degree 4x4 surface that results from a degree raise |

|
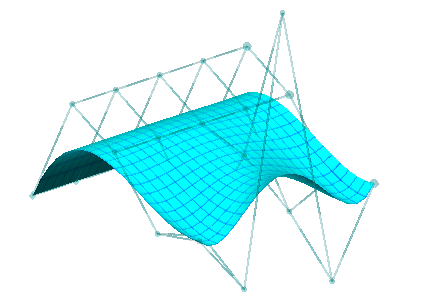
|
| Another degree raise in the other parametric direction gives us an equivalent degree 5x4 surface | Finally we make some control point adjustments to the degree 5x4 surface |
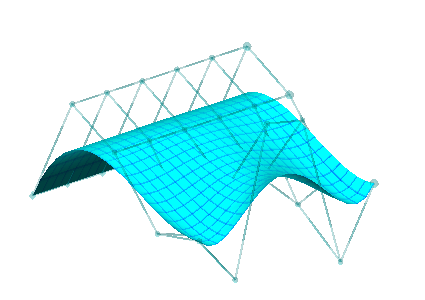
|
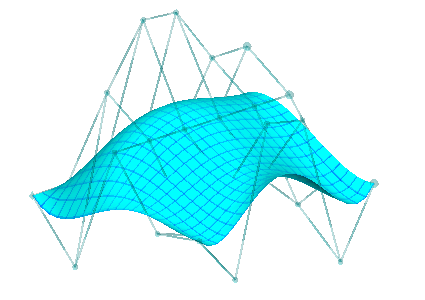
|
 |